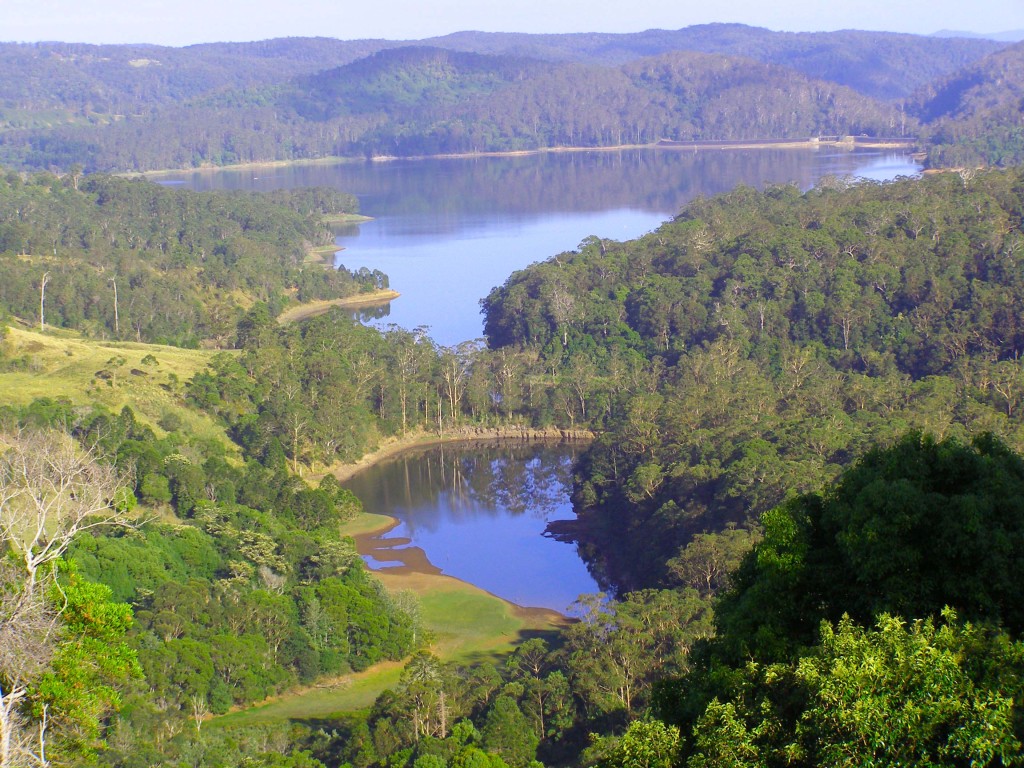
Lake Baroon catchment is 74.3 km2 in size (7,430 ha) and lies on the Blackall Ranges, within the Sunshine Coast Council district, in Queensland, Australia.
Construction of Lake Baroon was completed in November 1988. The Lake reached 100% capacity as a result of heavy rainfall during April 1989. High volumes of surface runoff and moderate erosion led to a blue green algal bloom in Lake Baroon in 1990.
Lake Baroon (also known as Baroon Pocket Dam) is an important, strategic water supply situated on South East Queensland’s Sunshine Coast. With an annual yield in excess of 20,000 ML/yr, Baroon Pocket Dam supplies all of Sunshine Coast Council’s potable water. The lake also supplies northern Brisbane via the Northern Pipeline Interconnector. High yearly rainfall ensures the dam rarely falls below 70% capacity.
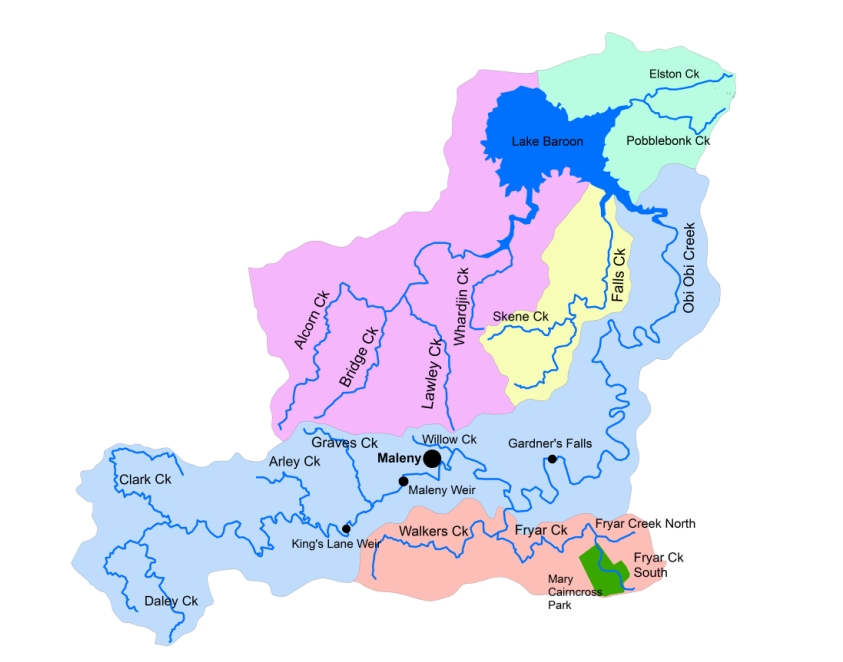 The catchment comprises a myriad of waterways dissecting the landscape, with five major waterways entering the lake (Obi Obi Creek, Walkers Creek, Bridge Creek, Falls Creek and Elston (also known as Smalls or Lexys) Creek. These waterways all drain into Lake Baroon.
The catchment comprises a myriad of waterways dissecting the landscape, with five major waterways entering the lake (Obi Obi Creek, Walkers Creek, Bridge Creek, Falls Creek and Elston (also known as Smalls or Lexys) Creek. These waterways all drain into Lake Baroon.
The quality of the water discharging into the lake is affected by a myriad of landuse across the catchment, including dairy and beef cattle, horses, horticultural production, natural vegetation, rural and urban residential, service provision and light industrial landuse.


